Isha Netralaya | Best Eye Hospital in Maharashtra | Eye Specialist
Diabetic Retinopathy
Understanding About Diabetic Retinopathy
Diabetic retinopathy is an eye condition that affects people with diabetes. It occurs when high blood sugar levels damage the blood vessels in the retina, the light-sensitive tissue at the back of the eye. Over time, this damage can lead to vision problems, including blindness if left untreated. Diabetic retinopathy usually develops in stages and can affect anyone with type 1 or type 2 diabetes, particularly those who have had diabetes for many years or have poorly controlled blood sugar levels.
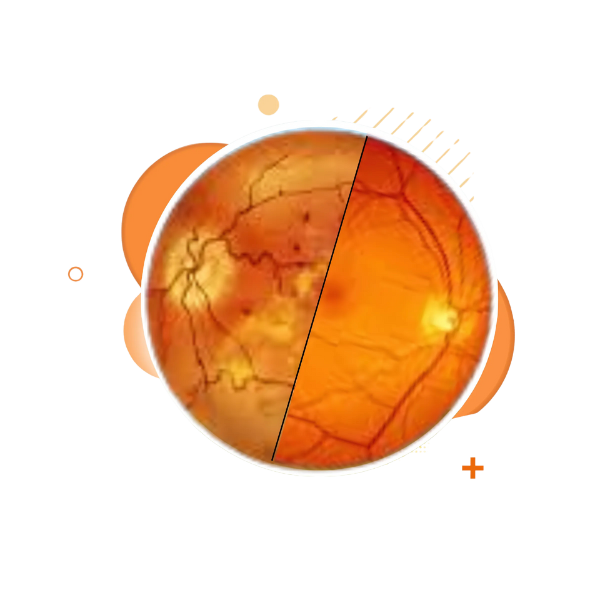
Types of Diabetic Retinopathy:
In the early stages, the blood vessels in the retina weaken and leak fluid or blood, causing swelling. NPDR can be mild, moderate, or severe, but it may not cause noticeable symptoms right away.
In the more advanced stage, new, abnormal blood vessels grow in the retina. These fragile vessels can bleed into the vitreous (the gel-like fluid inside the eye) and may lead to retinal detachment or permanent vision loss.
This occurs when fluid leaks into the macula, the central part of the retina responsible for sharp vision. DME can occur at any stage of diabetic retinopathy and leads to blurry or distorted vision.
Symptoms:
As the blood vessels in the retina become damaged, vision may become blurry or distorted.
You may notice dark spots, strings, or floaters drifting in your field of vision due to bleeding inside the eye.
Night vision may be impaired as the retina becomes damaged over time.
In severe cases, a sudden loss of vision may occur due to bleeding or retinal detachment.
Vision may become dull or colors may appear less vibrant as the condition progresses.
Treatment:
The most important treatment for diabetic retinopathy is controlling blood sugar levels. Proper diabetes management can slow the progression of the disease.
Laser therapy can seal leaking blood vessels and prevent the growth of abnormal vessels in the retina.
Medications such as anti-VEGF drugs are injected directly into the eye to reduce swelling and prevent the growth of abnormal blood vessels.
In advanced cases, a vitrectomy may be needed to remove blood or scar tissue from the vitreous and prevent retinal detachment.
Corticosteroid injections can help reduce swelling in the macula and improve vision in cases of diabetic macular edema.
Precautions:
People with diabetes should have a comprehensive dilated eye exam at least once a year to detect early signs of diabetic retinopathy.
High blood pressure and high cholesterol can worsen diabetic retinopathy, so it’s important to keep these conditions under control.
Maintaining healthy blood sugar levels is crucial in preventing or slowing the progression of diabetic retinopathy.
Smoking increases the risk of complications from diabetic retinopathy and should be avoided.
If you notice any sudden changes in your vision, such as blurriness or dark spots, contact your eye doctor immediately.
Before Surgery
Before undergoing surgery for diabetic retinopathy, your doctor will perform a detailed eye exam to assess the extent of the damage. Imaging tests like optical coherence tomography (OCT) or fluorescein angiography may be used to evaluate the retina. It’s important to discuss your overall health and blood sugar management with your doctor, as uncontrolled diabetes can affect healing and recovery. Your doctor may advise adjusting your medications before surgery and will explain the risks and benefits of the procedure, including the possibility of vision improvement or further complications.
During Surgery
During surgery, depending on the severity of your condition, different techniques may be used. Laser surgery, known as photocoagulation, involves using a laser to seal leaking blood vessels or prevent the growth of new, abnormal vessels. In more severe cases, a vitrectomy may be performed, where the surgeon removes the blood-filled vitreous gel from the eye and replaces it with a saline solution. The surgery is usually done under local anesthesia, and you may feel some pressure but no pain. The duration of the procedure varies based on the complexity of the case.
After Surgery
After surgery, your vision may be blurry for a few days, and you’ll need to use prescribed eye drops to prevent infection and promote healing. It’s important to avoid strenuous activities, heavy lifting, and bending over for at least a week after surgery to prevent pressure on the eye. You will have follow-up appointments to monitor the healing process and ensure the surgery was successful. It can take several weeks for your vision to stabilize, and in some cases, additional treatments may be needed to maintain vision. Controlling blood sugar levels remains critical to prevent further damage.
Isha Netralaya
As one of the leading eye hospitals in the heart of Thane, we take pride in our expertise in treating a varied range of eye problems.

LASIK Surgery
LASIK Surgery In Maharashtra

RETINA
RETINA Surgery In Maharashtra

CATARACT
Robotic Cataract Surgery

SQUINT
Specializes in Pediatric Squint

OCULOPLASTY
Best Oculoplastic surgeons in Thane

CORNEA
Advances Cornea Treatments in Thane

PEDIATRIC
Best Pediatric Ophthalmology Hospital

GLAUCOMA
Glaucoma Treatment In Maharashtra
Diabetic Retinopathy FAQs
No, once vision loss occurs, it cannot be fully reversed, but early detection and treatment can slow its progression and prevent further damage.
Diabetic retinopathy progresses gradually, often over several years. The speed of progression depends on how well blood sugar, blood pressure, and cholesterol levels are controlled.
Yes, if left untreated, diabetic retinopathy can cause blindness. However, with early detection and proper management, the risk of severe vision loss can be reduced.
Laser treatment is typically not painful, but you may feel slight discomfort or pressure during the procedure. Your eye will be numbed with anesthesia before the treatment.
People who have had diabetes for many years, particularly those with poorly controlled blood sugar levels, high blood pressure, or high cholesterol, are at the highest risk for developing diabetic retinopathy.




